Swagger/OpenAPI
Swagger is an open source set of specifications and tools for developing and describing REST APIs. RADKit Client can pull the OpenAPI specification from a Swagger enabled device, and use this information to perform REST API operations (Get, Post, Put, Delete) using the API paths provided in the specification. This feature guide first explains how to set up RADKit Service to access devices using Swagger. Then, it explains how to query the Swagger paths from the Client and how to process the results returned.
Note
The API authentication method and the location of the OpenAPI specification(s) are specific to every device type. For those devices that are not yet supported natively in RADKit, the alternative is to use the raw HTTP API and implement the appropriate authentication methods. For more details, see Raw HTTP API.
Note
Swagger is only supported on single devices at the moment.
Service configuration
To enable Swagger support, when either adding a new device, or editing an existing one, check
the Swagger box under Available Management Protocols. Subsequently, the Swagger
configuration section will appear:
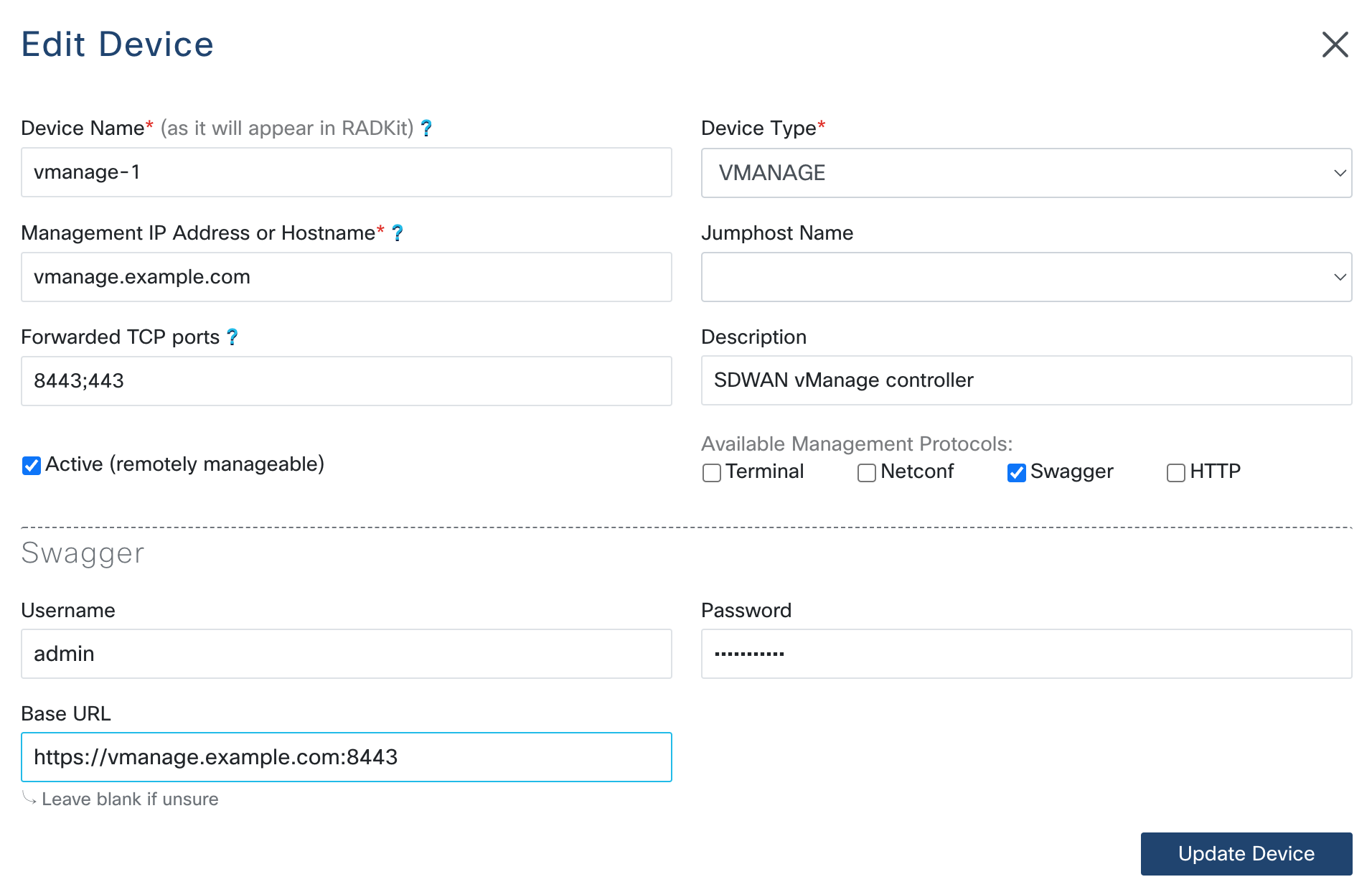
Base URL
The Base URL field can usually be left blank, however if the IP address or FQDN used to reach
the Swagger/OpenAPI endpoint is different from the one mentioned as Managed IP Address or Hostname,
then the base URL has to be provided. The exact URL depends on the device type, as shown in the list
below (keep in mind that any load-balancer or reverse proxy on the path may further alter the URL,
so please test with a browser from the same location as the Service and make adjustments as needed):
SD-WAN vManage:
https://<address>:8443ISE:
https://<address>:443RADKit Service:
https://<address>:8081CMS:
https://<address>:443CVP:
https://<address>:8111UCCE:
https://<address>:7890Expressway:
https://<address>:443HyperFlex:
https://<address>:443FMC:
https://<address>:443FTD:
https://<address>:443
Client operation
Devices Swagger status
When the Client loads the service inventory, it gets an internal attribute for each
device called swagger_config which is set to either True or False,
depending on whether the Service has Swagger credentials configured for that device:
>>> vmanage = service.inventory['vmanage-1']
>>> vmanage.attributes.internal
<radkit_client.sync.device.DeviceAttributesDict object at 0x106b97220>
key value
------------------- -------------
description vManage
device_type VMANAGE
forwarded_tcp_ports 8443;443
host 172.18.124.60
http_config True
netconf_config False
snmp_version None
swagger_config True
terminal_config False
Updating the Swagger API
Every Device object has a .swagger attribute which
represents the Swagger API for that device. By default this
radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerAPI object has a status of UNKNOWN:
>>> vmanage.swagger
[UNKNOWN] SwaggerAPI(status='UNKNOWN')
------ -------
status UNKNOWN
------ -------
For a list of all available status for Swagger API, see radkit_client.sync.SwaggerAPIStatus.
If the device has the Swagger credentials configured on the Service side, its capabilities
can be retrieved from the Client using
Device.update_swagger():
>>> vmanage.update_swagger().wait()
[SUCCESS] FillerRequest(status='SUCCESS', rpc_name='get-swagger-paths/2.0')
---------------- ---------------------------------
sent_timestamp 2022-08-17 14:46:58
request_type Swagger paths
client_id radkit-user@example.com
service_id xxxx-yyyy-zzzz
result None
forwarder wss://prod.radkit-cloud.cisco.com/forwarder-2
e2ee_used True
compression_used zstd
---------------- ---------------------------------
The result of this request contains more detailed information about the
swagger capabilities update.
>>> vmanage.update_swagger().wait().result
[SUCCESS] <radkit_client.sync.device.DeviceCapabilitiesUpdate object at 0xffff68f42a60>
----------- -------------------------
service_id xxxx-yyyy-zzzz
device_name vmanage
result Found 2516 swagger paths.
----------- -------------------------
If the retrieval is successful, the Swagger API status changes to AVAILABLE:
>>> vmanage.swagger
[AVAILABLE] SwaggerAPI(status='AVAILABLE')
------ ---------
status AVAILABLE
------ ---------
Note that it’s also possible to call DeviceDict.update_swagger() on a DeviceDict to load the Swagger capabilities of
multiple devices at once.
Exploring Swagger paths
Once the Swagger API status becomes AVAILABLE, the API paths supported by
Swagger can be retrieved from SwaggerAPI.paths,
which is a dictionary where the key is the path and the value is a
radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerPath:
>>> device.swagger.paths
<radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerPathsDict object at 0x7f102c5204f0>
path verbs
---------------------------------------- ----------------------
/admins GET, PUT, POST, DELETE
/admins/bulk PUT, POST, DELETE
/admins/change_password PUT
/admins/count GET
/admins/me GET
...
The supported API operations for a given path can be displayed with:
>>> vmanage.swagger.paths['/admin/user']
Path: /admin/user
Operations:
- [GET]
Get all users
(This operation takes no parameters)
- [POST]
Create a user
Pass payload using .post(json=...)
>>> vmanage.swagger.paths['/admin/user'].operations
<radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerPathOperationsDict object at 0x110beb750>
verb description
------ -------------
GET Get all users
POST Create a user
>>> vmanage.swagger.paths['/admin/user'].operations['GET']
SwaggerPathOperation(description=description='Get all users')
----------- -------------
description Get all users
parameters (none)
----------- -------------
Note
When building the list of Swagger paths and their parameters, if RADKit Client encounters
a parameter name that is a reserved Python keyword, it will append an underscore _ to the
name; e.g. as becomes as_. Also, if a parameter name contains non-alphanumerical characters,
those will be replaced by an underscore _.
Perform operations on an API path
To perform desired operations on an API path, use one of the supported API methods.
Here is an example to perform a get() operation:
>>> vmanage.swagger.paths['/device/system/status']
Path: /device/system/status
Operations:
- [GET]
Get device system status list (Real Time)
Parameters:
- 'deviceId' [required]
Device IP
>>> req = vmanage.swagger.paths['/device/system/status'].get(deviceId = '6.1.1.11')
Some Swagger API paths have the required parameter in the API path itself. In the following example,
the deviceCategory is a required parameter:
>>> vmanage.swagger.paths['/system/device/{deviceCategory}']
Path: /system/device/{deviceCategory}
Operations:
- [GET]
Get devices details. When {deviceCategory = controllers}, it returns vEdge sync status, vBond, vManage and vSmart. When {deviceCategory = vedges}, it returns all available vEdge routers
Parameters:
- 'deviceCategory' [required]
Device category
- 'model'
Device model
- 'state'
List of states
- 'uuid'
List of device uuid
- 'deviceIP'
List of device system IP
- 'validity'
List of device validity
- 'family'
The platform family to filter for
- 'siteId'
The Site Id to filter for
- 'topology'
The device topology to filter for
- 'tag'
The tag name to filter for
Since these API paths are essentially keys to the API paths dictionary, in order to perform the get()
operation with the required parameter for this API path, use the following:
>>> req = vmanage.swagger.paths['/system/device/{deviceCategory}'].get(deviceCategory='controllers').wait()
The get() operation returns an instance of radkit_client.sync.request.FillerRequest, which
represents the request sent from Client to Service for the Swagger API call.
>>> req
[DELIVERED] FillerRequest(status='DELIVERED', rpc_name='call-swagger-path/2.0')
---------------- --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sent_timestamp 2022-08-17 19:43:22
request_type Swagger path query
client_id radkit_user@example.com
service_id xxxx-yyyy-zzzz
updates 0 total, 0 failed
result AsyncSwaggerResponse(device=AsyncDevice(name='vmanage-1', service_display-nam...
forwarder wss://prod.radkit-cloud.cisco.com/forwarder-2/
e2ee_used True
compression_used zstd
---------------- --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Here is another example of performing a post() operation to add a new user:
>>> new_user = {
"userName": "testuser", "password": "secret_pass",
"description": "a new user", "locale": "en_US", "group": ["netadmin"]
}
>>> req = vmanage.swagger.paths['/admin/user'].post(json=new_user).wait()
>>> req.result.status_code
200
>>> req.result.content
b'{}'
In this example, the status code returned by the API post() call indicates the call was successful.
If the API call fails, then .result.content would include the error message in the API response. Please see below
for more information on how to process the Swagger API response.
The post, put and patch methods also support sending data in different formats than JSON:
# Request with binary data
>>> r = httpbin.swagger.paths['//post'].post(content=b"binary content").wait()
>>> r.result.json
{
"args": {},
"data": "binary content",
"files": {},
"form": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"Content-Length": "14",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "python-httpx/0.23.0",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6389a0f1-1bbceddf2d066f9b62fa537c",
},
"json": None,
"origin": "173.38.220.39",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/post",
}
# Request with form encoded data
>>> r = httpbin.swagger.paths['//post'].post(data={"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2"}).wait()
>>> r.result.json
{
"args": {},
"data": "",
"files": {},
"form": {"key1": "b'value1'", "key2": "b'value2'"},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"Content-Length": "37",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "python-httpx/0.23.0",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6389a129-71f0bf674ee14a2a69b0c263",
},
"json": None,
"origin": "173.38.220.39",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/post",
}
# Request with multipart file upload
>>> r = httpbin.swagger.paths['//post'].post(files={"upload-file": ("hello.py", open("hello.py", "rb"))}).wait()
>>> r.result.json
{
"args": {},
"data": "",
"files": {"upload-file": 'print("Hello World")\n'},
"form": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"Content-Length": "208",
"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=9d85fa88395b156f9170947f2bbd10a2",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "python-httpx/0.23.0",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6389a842-21267add7cb6fc7764281e98",
},
"json": None,
"origin": "173.38.220.39",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/post",
}
Note
The examples above were created with the device which is proxy to the http://httpbin.org
Direct Swagger API access
Previously we used radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerAPI.paths to explore the Swagger API paths
and supported API operations. Alternatively, RADKit also allows direct access to an API path if the
path is known by other means, e.g., for SDWAN vManage by using the
vManage API Reference. The
supported operations are:
SwaggerAPI.get()SwaggerAPI.put()SwaggerAPI.post()SwaggerAPI.delete()SwaggerAPI.patch()
Here is an example of a direct API get() operation on /device/system/status with an input parameter
of deviceID:
>>> req = vmanage.swagger.get('/device/system/status', {deviceId: "6.1.1.11"})
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(req.result.json)
{'data': [{'board_type': 'Vedge-CSR',
'bootloader_version': 'Not applicable',
'build_number': 'Not applicable',
...
Processing the Swagger response
As with all RADKit requests, a Swagger request will have an associated result object.
The Swagger response will be stored in result.content as bytes. To convert it
into a Python object, the result.json property can be used.
>>> req = vmanage.swagger.get('/device/system/status', {"deviceId": "6.1.1.11"})
>>> req.result.content
b'{"header":{"generatedOn":1660934774631,"viewKeys":{"uniqueKey":["vdevice-dataKey"],"preferenceKey":"grid-SystemStatus"},"columns":...
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(req.result.json)
{'data': [{'board_type': 'Vedge-CSR',
'bootloader_version': 'Not applicable',
'build_number': 'Not applicable',
'chassis-serial-number': 'SSI130300YK',
'config_date/date-time-string': 'Fri Aug 19 14:46:14 EDT 2022',
...
Alternatively, the json object can be converted to a json string and then printed for a better visual representation:
>>> import json
>>> print(json.dumps(req.result.json, indent=4))
{
"header": {
"generatedOn": 1724706125439,
"viewKeys": {
"uniqueKey": [
"vdevice-dataKey"
],
"preferenceKey": "grid-SystemStatus"
},
...
Client metadata
Some Swagger clients offer metadata.
The metadata are fetched during Device.update_swagger()
and can be accessed by SwaggerAPI.metadata <radkit_client.sync.swagger.SwaggerAPI.metadata>:
>>> fmc.update_swagger().wait()
[SUCCESS] FillerRequest(status='SUCCESS', rpc_name='get-swagger-paths/2.0')
---------------- ---------------------------------
sent_timestamp 2022-08-17 14:46:58
request_type Swagger paths
client_id radkit-user@example.com
service_id xxxx-yyyy-zzzz
result None
forwarder wss://prod.radkit-cloud.cisco.com/forwarder-2
e2ee_used True
compression_used zstd
---------------- ---------------------------------
>>> pprint(fmc.swagger.metadata)
{'domain_id': '111',
'domain_uuid': 'e276abec-e0f2-11e3-8169-6d9ed49b625f',
'domains': {'Global': 'e276abec-e0f2-11e3-8169-6d9ed49b625f'},
'user_uuid': '68d03c42-d9bd-11dc-89f2-b7961d42c462'}